Dextrose 50% Abboject®, Ansyr™ Syringe
Find Dextrose 50% Abboject®, Ansyr™ Syringe medical information:
Find Dextrose 50% Abboject®, Ansyr™ Syringe medical information:
Dextrose 50% Abboject®, Ansyr™ Syringe Quick Finder
Indications and Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
50% Dextrose Injection is indicated in the treatment of insulin hypoglycemia (hyperinsulinemia or insulin shock) to restore blood glucose levels.
The solution is also indicated, after dilution, for intravenous infusion as a source of carbohydrate calories in patients whose oral intake is restricted or inadequate to maintain nutritional requirements. Slow infusion of hypertonic solutions is essential to ensure proper utilization of dextrose and avoid production of hyperglycemia.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For peripheral vein administration:
Injection of the solution should be made slowly.
The maximum rate at which dextrose can be infused without producing glycosuria is 0.5 g/kg of body weight/hour. About 95% of the dextrose is retained when infused at a rate of 0.8 g/kg/hr.
In insulin-induced hypoglycemia, intravenous injection of 10 to 25 grams of dextrose (20 to 50 mL of 50% dextrose) is usually adequate. Repeated doses and supportive treatment may be required in severe cases. A specimen for blood glucose determination should be taken before injecting the dextrose. In such emergencies, dextrose should be administered promptly without awaiting pretreatment test results.
For central venous administration:
For total parenteral nutrition 50% Dextrose Injection, USP is administered by slow intravenous infusion (a) after admixture with amino acid solutions via an indwelling catheter with the tip positioned in a large central vein, preferably the superior vena cava, or (b) after dilution with sterile water for injection. Dosage should be adjusted to meet individual patient requirements.
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation.
The maximum rate of dextrose administration which does not result in glycosuria is the same as cited above.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. See CONTRAINDICATIONS.
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
A concentrated dextrose solution should not be used when intracranial or intraspinal hemorrhage is present, nor in the presence of delirium tremens if the patient is already dehydrated.
Dextrose injection without electrolytes should not be administered simultaneously with blood through the same infusion set because of the possibility that pseudoagglutination of red cells may occur.
Warnings and Precautions
WARNINGS
50% Dextrose Injection is hypertonic and may cause phlebitis and thrombosis at the site of injection.
Significant hyperglycemia and possible hyperosmolar syndrome may result from too rapid administration. The physician should be aware of the symptoms of hyperosmolar syndrome, such as mental confusion and loss of consciousness, especially in patients with chronic uremia and those with known carbohydrate intolerance.
The intravenous administration of this solution can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema.
Additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist if available. When introducing additives, use aseptic technique, mix thoroughly and do not store.
PRECAUTIONS
Do not use unless the solution is clear and seal is intact. Discard unused portion.
Electrolyte deficits, particularly in serum potassium and phosphate, may occur during prolonged use of concentrated dextrose solutions. Blood electrolyte monitoring is essential and fluid and electrolyte imbalances should be corrected. Essential vitamins and minerals also should be provided as needed.
To minimize hyperglycemia and consequent glycosuria, it is desirable to monitor blood and urine glucose and if necessary, add insulin.
When a concentrated dextrose infusion is abruptly withdrawn, it is advisable to follow with the administration of 5% or 10% dextrose injection to avoid rebound hypoglycemia.
Solutions containing dextrose should be used with caution in patients with known subclinical or overt diabetes mellitus.
Care should be exercised to ensure that the needle is well within the lumen of the vein and that extravasation does not occur. If thrombosis should occur during administration, the injection should be stopped and corrective measures instituted.
Concentrated dextrose solutions should not be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Studies with solutions in polypropylene syringes have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility.
Adverse Reactions
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hyperosmolar syndrome, resulting from excessively rapid administration of concentrated dextrose may cause mental confusion and/or loss of consciousness.
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and hypervolemia.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
Overdosage
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overhydration or solute overload during therapy, re-evaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures. See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
Description
DESCRIPTION
50% Dextrose Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, hypertonic solution of dextrose in water for injection for intravenous injection as a fluid and nutrient replenisher.
Each mL of fluid contains 0.5 g dextrose, hydrous which delivers 3.4 kcal/gram. The solution has an osmolarity of 2.53 mOsmol/mL (calc.), pH 3.2 to 6.5 and may contain sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment.
The solution contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer (except for pH adjustment) and is intended only for use as a single-dose injection. When smaller doses are required, the unused portion should be discarded with the entire unit.
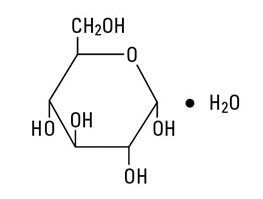
Dextrose, USP is chemically designated C6H12O6 ∙ H2O (D-glucose monohydrate), a hexose sugar freely soluble in water.
Dextrose, hydrous has the following structural formula:
Water for Injection, USP is chemically designated H2O.
The syringe is molded from a specially formulated polypropylene. Water permeates from inside the container at an extremely slow rate which will have an insignificant effect on solution concentration over the expected shelf life. Solutions in contact with the plastic container may leach out certain chemical components from the plastic in very small amounts; however, biological testing was supportive of the safety of the syringe material.
Clinical Pharmacology
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
When administered intravenously this solution restores blood glucose levels in hypoglycemia and provides a source of carbohydrate calories.
Carbohydrate in the form of dextrose may aid in minimizing liver glycogen depletion and exerts a protein-sparing action. Dextrose injection undergoes oxidation to carbon dioxide and water.
Water is an essential constituent of all body tissues and accounts for approximately 70% of total body weight. Average normal adult requirement ranges from two to three liters (1.0 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production).
Water balance is maintained by various regulatory mechanisms. Water distribution depends primarily on the concentration of electrolytes in the body compartments and sodium (Na+) plays a major role in maintaining physiologic equilibrium.
How Supplied/Storage and Handling
HOW SUPPLIED
50% Dextrose Injection, USP is supplied in single-dose containers as follows:
| Unit of Sale and Product Description | Strength (Concentration) | NDC |
|---|---|---|
Bundle of 10 | 25 g/50 mL | 0409-4902-34 |
Bundle of 10 | 25 g/50 mL | 0409-0505-25 |
Tray of 25 | 25 g/50 mL | 0409-6648-02 |
Bundle of 10 | 25 g/50 mL | 0409-7517-16 |
Other
NOTE: This solution is hypertonic - See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
LifeShield Abboject Syringe
Abboject Syringe
Fliptop Container
Ansyr II Plastic Syringe
Rx only
Abboject is a trademark of Abbott Laboratories.
LifeShield is the trademark of ICU Medical, Inc. and is used under license.
For Medical Information about 50% Dextrose Injection, please visit www.pfizermedinfo.com or call 1‑800-438-1985.
Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA
LAB-1027-7.0
Revised: July 2024
Resources
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Contact us.
Chat online with Pfizer Medical Information regarding your inquiry on a Pfizer medicine.
*Contact Medical Information. 9AM-5PM ET Monday to Friday; excluding holidays.
Report Adverse Event
Pfizer Safety
To report an adverse event related to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, and you are not part of a clinical trial* for this product, click the link below to submit your information:
Pfizer Safety Reporting Site*If you are involved in a clinical trial for this product, adverse events should be reported to your coordinating study site.
If you cannot use the above website, or would like to report an adverse event related to a different Pfizer product, please call Pfizer Safety at (800) 438-1985.
FDA Medwatch
You may also contact the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) directly to report adverse events or product quality concerns either online at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call (800) 822-7967.