SOMAVERT® WITH PREFILLED DILUENT SYRINGE Clinical Studies
(pegvisomant with PREFILLED DILUENT SYRINGE)
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
A total of one hundred twelve patients (63 men and 49 women) with acromegaly participated in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multi-center study comparing placebo and SOMAVERT. The mean ±SD age was 48±14 years, and the mean duration of acromegaly was 8±8 years. Ninety three had undergone previous pituitary surgery, of which 57 had also been treated with conventional radiation therapy. Six patients had undergone irradiation without surgery, nine had received only drug therapy, and four had received no previous therapy. At study start, the mean ± SD time since the subjects' last surgery and/or irradiation therapy, respectively, was 6.8 ± 0.93 years (n=63) and 5.6 ± 0.57 years (n=93).
Subjects were qualified for enrollment if their serum IGF-1, drawn after the required drug washout period, was ≥1.3 times the upper limit of the age-adjusted normal range. They were randomly assigned at the baseline visit to one of four treatment groups: placebo (n=32), 10 mg/day (n=26), 15 mg/day (n= 26), or 20 mg/day (n=28) of SOMAVERT subcutaneously IGF-1. The primary efficacy endpoint was IGF-1 percent change in IGF-1 concentrations from baseline to week 12. The three groups that received SOMAVERT showed statistically significant (p<0.01) reductions in serum levels of IGF-1 compared with the placebo group (Table 4).
| Placebo n=31 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=26 | 20 mg/day n=28 | ||
| ||||
Mean baseline IGF-1 (ng/ml) (SD) | 670 (288) | 627 (251) | 649 (293) | 732 (205) |
Mean percent change from baseline in IGF-1 (SD) | -4.0 (17) | -27 (28) | -48 (26) | -63 (21) |
SOMAVERT minus Placebo | -23* | -44* | -59* | |
There were also reductions in serum levels of free IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and ALS compared with placebo at all post-baseline visits (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Effects of SOMAVERT on Serum Markers (Mean ± Standard Error)
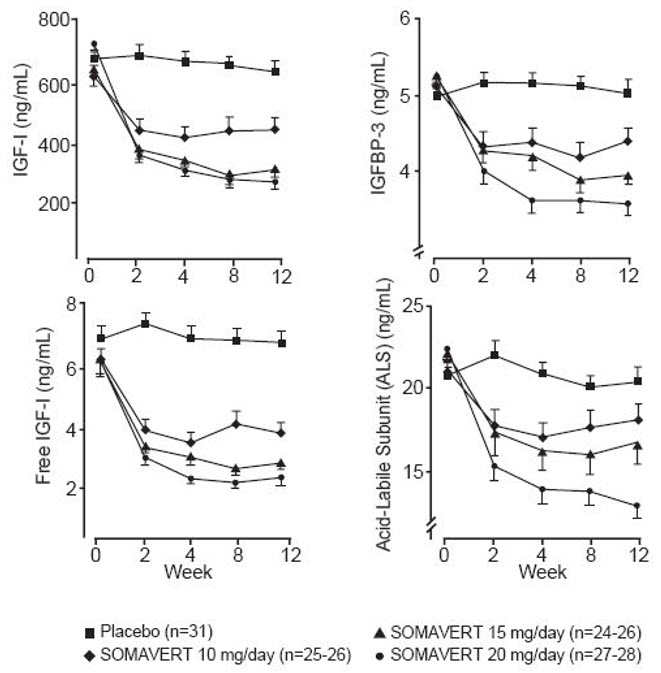 |
After 12 weeks of treatment, the following percentages of patients had normalized IGF-1 (Figure 2):
Figure 2. Percent of Patients Whose IGF-1 Levels Normalized at Week 12
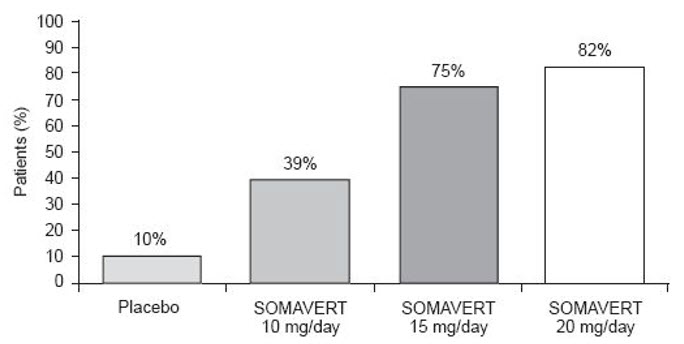 |
Table 5 shows the effect of treatment with SOMAVERT on ring size (standard jeweler's sizes converted to a numeric score ranging from 1 to 63), and on signs and symptoms of acromegaly. Each individual score for a sign or symptom of acromegaly (for soft-tissue swelling, arthralgia, headache, perspiration and fatigue) was based on a nine-point ordinal rating scale (0 = absent and 8 = severe and incapacitating), and the total score for signs or symptoms of acromegaly was derived from the sum of the individual scores. Mean baseline scores were as follows: ring size = 47.1; total signs and symptoms = 15.2; soft tissue swelling = 2.5; arthralgia = 3.2; headache = 2.4; perspiration = 3.3; and fatigue = 3.7.
| Placebo n=30 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=24–25 | 20 mg/day n=26–27 | ||
Ring size | -0.1 (2.3) | -0.8 (1.6) | -1.9 (2.0) | -2.5 (3.3) |
Total score for signs and symptoms of acromegaly | 1.3 (6.0) | -2.5 (4.3) | -4.4 (5.9) | -4.7 (4.7) |
Soft-tissue swelling | 0.3 (2.3) | -0.7 (1.6) | -1.2 (2.3) | -1.3 (1.3) |
Arthralgia | 0.1 (1.8) | -0.3 (1.8) | -0.5 (2.5) | -0.4 (2.1) |
Headache | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.4 (1.6) | -0.3 (1.4) | -0.3 (2.0) |
Perspiration | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.6 (1.6) | -1.1 (1.3) | -1.7 (1.6) |
Fatigue | 0.7 (1.5) | -0.5 (1.4) | -1.3 (1.7) | -1.0 (1.6) |
Serum growth hormone (GH) concentrations, as measured by research assays using antibodies that do not cross-react with pegvisomant, rose within two weeks of beginning treatment with SOMAVERT. The largest increase in GH concentration was seen in patients treated with doses of SOMAVERT 20 mg/day. This effect is presumably the result of diminished inhibition of GH secretion as IGF-1 levels fall. As shown in Figure 3, when patients with acromegaly were given a loading dose of SOMAVERT followed by a fixed daily dose, the rise in GH was inversely proportional to the fall in IGF-1 and generally stabilized by week 2. Serum GH concentrations remained stable in patients treated with SOMAVERT for the average of 43 weeks (range, 0–82 weeks).
Figure 3. Percent Change in Serum GH and IGF-1 Concentrations
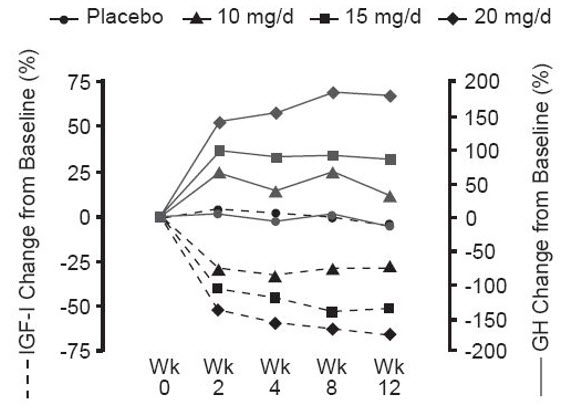 |
In the open-label extension to the clinical study, 109 subjects (including 6 new patients) with mean treatment exposure of 42.6 weeks (range 1 day – 82 weeks), 93 (85.3%) subjects had an adverse event, 16 (14.7%) had an SAE, and 4 (3.7%) discontinued due to an AE (headaches, elevated liver function tests, pancreatic cancer, and weight gain). A total of 100 (92.6%) of the 108 subjects with available IGF-1 data had a normal IGF-1 concentration at any visit during the study.
Find SOMAVERT® WITH PREFILLED DILUENT SYRINGE medical information:
Find SOMAVERT® WITH PREFILLED DILUENT SYRINGE medical information:
SOMAVERT® WITH PREFILLED DILUENT SYRINGE Quick Finder
Health Professional Information
Clinical Studies
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
A total of one hundred twelve patients (63 men and 49 women) with acromegaly participated in a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multi-center study comparing placebo and SOMAVERT. The mean ±SD age was 48±14 years, and the mean duration of acromegaly was 8±8 years. Ninety three had undergone previous pituitary surgery, of which 57 had also been treated with conventional radiation therapy. Six patients had undergone irradiation without surgery, nine had received only drug therapy, and four had received no previous therapy. At study start, the mean ± SD time since the subjects' last surgery and/or irradiation therapy, respectively, was 6.8 ± 0.93 years (n=63) and 5.6 ± 0.57 years (n=93).
Subjects were qualified for enrollment if their serum IGF-1, drawn after the required drug washout period, was ≥1.3 times the upper limit of the age-adjusted normal range. They were randomly assigned at the baseline visit to one of four treatment groups: placebo (n=32), 10 mg/day (n=26), 15 mg/day (n= 26), or 20 mg/day (n=28) of SOMAVERT subcutaneously IGF-1. The primary efficacy endpoint was IGF-1 percent change in IGF-1 concentrations from baseline to week 12. The three groups that received SOMAVERT showed statistically significant (p<0.01) reductions in serum levels of IGF-1 compared with the placebo group (Table 4).
| Placebo n=31 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=26 | 20 mg/day n=28 | ||
| ||||
Mean baseline IGF-1 (ng/ml) (SD) | 670 (288) | 627 (251) | 649 (293) | 732 (205) |
Mean percent change from baseline in IGF-1 (SD) | -4.0 (17) | -27 (28) | -48 (26) | -63 (21) |
SOMAVERT minus Placebo | -23* | -44* | -59* | |
There were also reductions in serum levels of free IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and ALS compared with placebo at all post-baseline visits (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Effects of SOMAVERT on Serum Markers (Mean ± Standard Error)
 |
After 12 weeks of treatment, the following percentages of patients had normalized IGF-1 (Figure 2):
Figure 2. Percent of Patients Whose IGF-1 Levels Normalized at Week 12
 |
Table 5 shows the effect of treatment with SOMAVERT on ring size (standard jeweler's sizes converted to a numeric score ranging from 1 to 63), and on signs and symptoms of acromegaly. Each individual score for a sign or symptom of acromegaly (for soft-tissue swelling, arthralgia, headache, perspiration and fatigue) was based on a nine-point ordinal rating scale (0 = absent and 8 = severe and incapacitating), and the total score for signs or symptoms of acromegaly was derived from the sum of the individual scores. Mean baseline scores were as follows: ring size = 47.1; total signs and symptoms = 15.2; soft tissue swelling = 2.5; arthralgia = 3.2; headache = 2.4; perspiration = 3.3; and fatigue = 3.7.
| Placebo n=30 | SOMAVERT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/day n=26 | 15 mg/day n=24–25 | 20 mg/day n=26–27 | ||
Ring size | -0.1 (2.3) | -0.8 (1.6) | -1.9 (2.0) | -2.5 (3.3) |
Total score for signs and symptoms of acromegaly | 1.3 (6.0) | -2.5 (4.3) | -4.4 (5.9) | -4.7 (4.7) |
Soft-tissue swelling | 0.3 (2.3) | -0.7 (1.6) | -1.2 (2.3) | -1.3 (1.3) |
Arthralgia | 0.1 (1.8) | -0.3 (1.8) | -0.5 (2.5) | -0.4 (2.1) |
Headache | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.4 (1.6) | -0.3 (1.4) | -0.3 (2.0) |
Perspiration | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.6 (1.6) | -1.1 (1.3) | -1.7 (1.6) |
Fatigue | 0.7 (1.5) | -0.5 (1.4) | -1.3 (1.7) | -1.0 (1.6) |
Serum growth hormone (GH) concentrations, as measured by research assays using antibodies that do not cross-react with pegvisomant, rose within two weeks of beginning treatment with SOMAVERT. The largest increase in GH concentration was seen in patients treated with doses of SOMAVERT 20 mg/day. This effect is presumably the result of diminished inhibition of GH secretion as IGF-1 levels fall. As shown in Figure 3, when patients with acromegaly were given a loading dose of SOMAVERT followed by a fixed daily dose, the rise in GH was inversely proportional to the fall in IGF-1 and generally stabilized by week 2. Serum GH concentrations remained stable in patients treated with SOMAVERT for the average of 43 weeks (range, 0–82 weeks).
Figure 3. Percent Change in Serum GH and IGF-1 Concentrations
 |
In the open-label extension to the clinical study, 109 subjects (including 6 new patients) with mean treatment exposure of 42.6 weeks (range 1 day – 82 weeks), 93 (85.3%) subjects had an adverse event, 16 (14.7%) had an SAE, and 4 (3.7%) discontinued due to an AE (headaches, elevated liver function tests, pancreatic cancer, and weight gain). A total of 100 (92.6%) of the 108 subjects with available IGF-1 data had a normal IGF-1 concentration at any visit during the study.
Health Professional Information
{{section_name_patient}}
{{section_body_html_patient}}
Resources
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Contact us.
Chat online with Pfizer Medical Information regarding your inquiry on a Pfizer medicine.
*Speak with a Pfizer Medical Information Professional regarding your medical inquiry. Available 9AM-5Pm ET Monday to Friday; excluding holidays.
Submit a medical question for Pfizer prescription products.
Report Adverse Event
To report an adverse event related to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, and you are not part of a clinical trial* for this product, click the link below to submit your information:
Pfizer Safety Reporting Site*If you are involved in a clinical trial for this product, adverse events should be reported to your coordinating study site.
If you cannot use the above website, or would like to report an adverse event related to a different Pfizer product, please call Pfizer Safety at (800) 438-1985.
You may also contact the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) directly to report adverse events or product quality concerns either online at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call (800) 822-7967.